
Originally published on fastradius.com on May 15, 2020
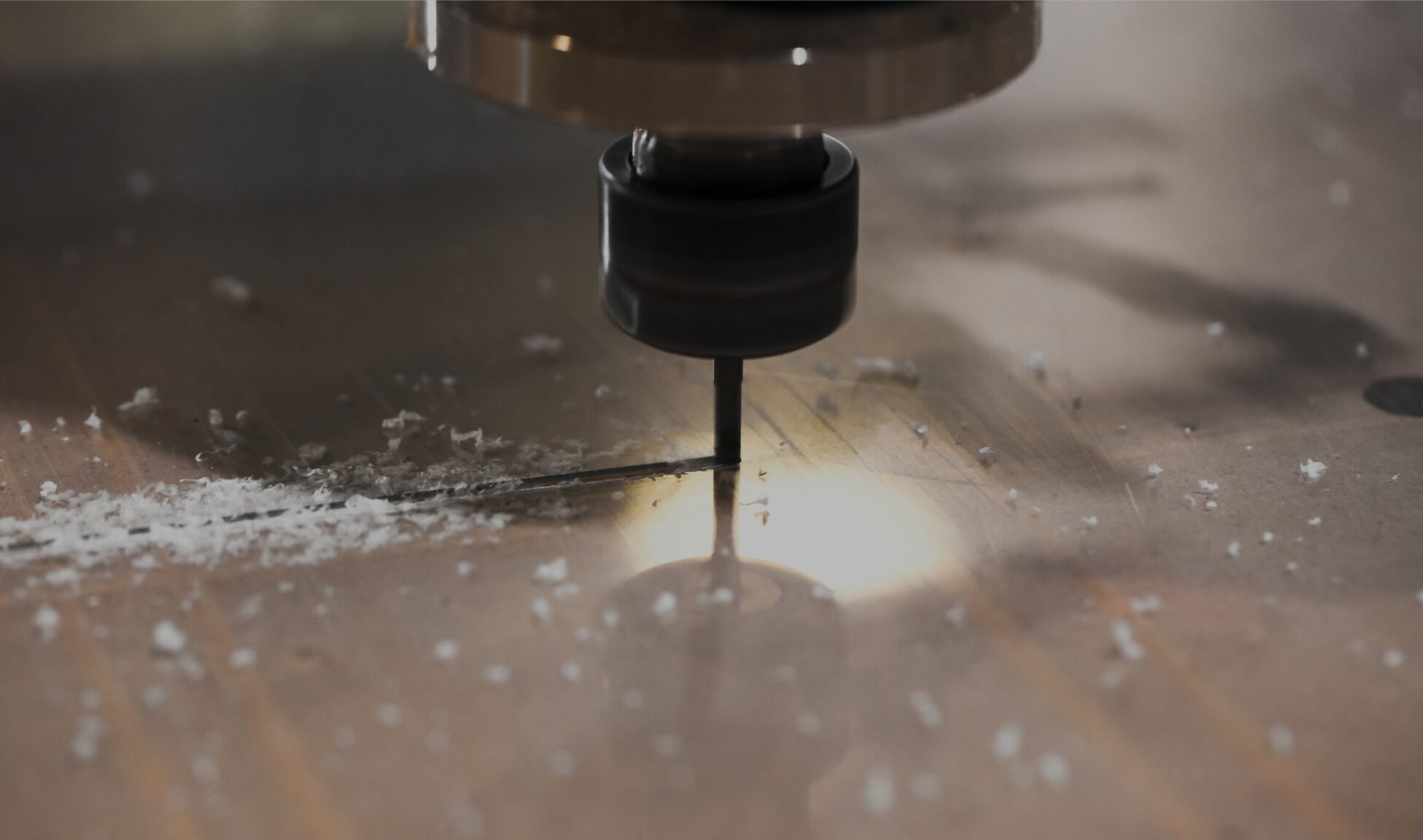
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that forms a completed part by steadily drilling, turning, or milling away thin layers from a solid block of metal or plastic. A Computer Aided Design (CAD) file guides the computer-controlled cutting tool down a set tool path to shape the final part.
Since a computer is responsible for most of the machining during this process, the process is known for quick turnaround and for producing high-quality, uniform parts. What’s more, CNC machining can produce parts with some of the tightest tolerances possible.
However, there are a few key limitations that engineers and product designers should keep in mind when considering CNC machining for plastic parts. The most significant drawback of CNC machining is often cost. Although CNC machining operating costs vary by method initial startup costs can be high across the board. As such, this manufacturing process is unlikely to be cost-effective outside of medium to high volume production runs.
While no manufacturing process is perfect, CNC machining offers numerous benefits that make it an excellent choice for many parts. Product managers and engineers should consider employing CNC machining for the following plastic applications.
Plastic CNC machining is an excellent choice for medical devices and components due to the inherent precision afforded by the method. Medical device manufacturers trust CNC machining to produce identical, intricate parts reliably.
The design flexibility allowed by the process is also advantageous. Engineers can easily change or manipulate digital design files to achieve their desired part, rendering the creation of personalized medical devices like dental surgical guides or cardiac implants quick and easy. Further, there are many off the shelf medical-grade materials available for CNC machining.
As U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations evolve and consumers increasingly demand healthy, sustainable food and beverage manufacturing, the demand for high-quality food service equipment is higher than ever. Food and beverage industry manufacturers need parts that are tough enough to work around the clock, but safe and gentle enough to come into contact with the foods people eat every day.
CNC machining helps engineers achieve this delicate balance. Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), a popular plastic used in CNC machining, is a stain-, wear-, odor-, and solvent-resistant plastic that meets all FDA, USDA, and 3-A Dairy requirements. It can be used to make everything from spray bars to assembly line parts.
Semiconductive parts offer an intermediate level of electrical conductivity, classified somewhere between a conductor and an insulator. Semiconductive parts are used in a range of electronic devices, including diodes, integrated circuits, transistors, and more. They are shockproof, typically compact, and can last almost a lifetime.
Building these parts would not be possible without plastic CNC machining. Semiconductor parts and assemblies are often highly intricate and demand extremely tight tolerances and high-polish surface finishes. The precision and mechanical strength enabled by CNC machining make this process ideal for the production of such parts. Plastic CNC machining produces tough parts with excellent electrical properties, which is ideal for applications such as electrical insulators, small circuits, gaskets, and watertight seals.
When it comes to manufacturing high-performance engineering parts and components for automotive and aerospace applications, CNC machining is an ideal method due to the wide variety of available plastics that meet strict regulations.
For example, ULTEM® (PEI) can perform at temperatures above 400°F and is frequently used to create fire blockers, airplane seat covers, and turbine engines. Plastic CNC machining might be one of the more expensive manufacturing processes available, but aerospace engineers can’t put a price on strength and durability when it comes to mission-critical parts.
Plastic CNC machining can also be used to conduct functional testing when a small batch of a prospective parts must be made with the final material before beginning the injection molding process.
Suppose an engineer has a design for a custom gear that will be mass-produced using injection-molded polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). The engineer may be inclined to test the part by 3D printing it first; unfortunately, however, PTFE isn’t 3D printable. CNC machining, on the other hand, is compatible with a much broader range of materials, including PTFE.
With CNC machining, engineers and product teams can machine a number of parts in the final material, conduct functional testing, verify the design, then release the design for mass production via injection molding.
While it often requires high upfront costs, CNC machining provides advantages that other methods simply cannot match.
Here at SyBridge, we can work with you to determine if your part is a good candidate for plastic CNC machining or any other manufacturing process. We help our customers evaluate their project requirements and find the best technology for the job. Let’s make new things possible — contact us today.
Forget typical cycle times. We're pushing the boundaries of conformal cooling. While traditional approaches deliver…
Forget typical cycle times. We're pushing the boundaries of conformal cooling. While traditional approaches deliver…
From left to right: Brayden Janak (apprentice); Logan Vifaquain (CNC machining, Programming and CMM); Ron…
SyBridge Technologies is proud to announce we have been awarded the 2023 General Motors Supplier…
Today, designers and engineers are accustomed to working with digital tools in their day-to-day jobs.…
Optimizing Your Injection Molding Process for Cost-Effective Manufacturing Excellence In today’s competitive landscape, manufacturers are…