
Originally published on fastradius.com on June 29, 2020
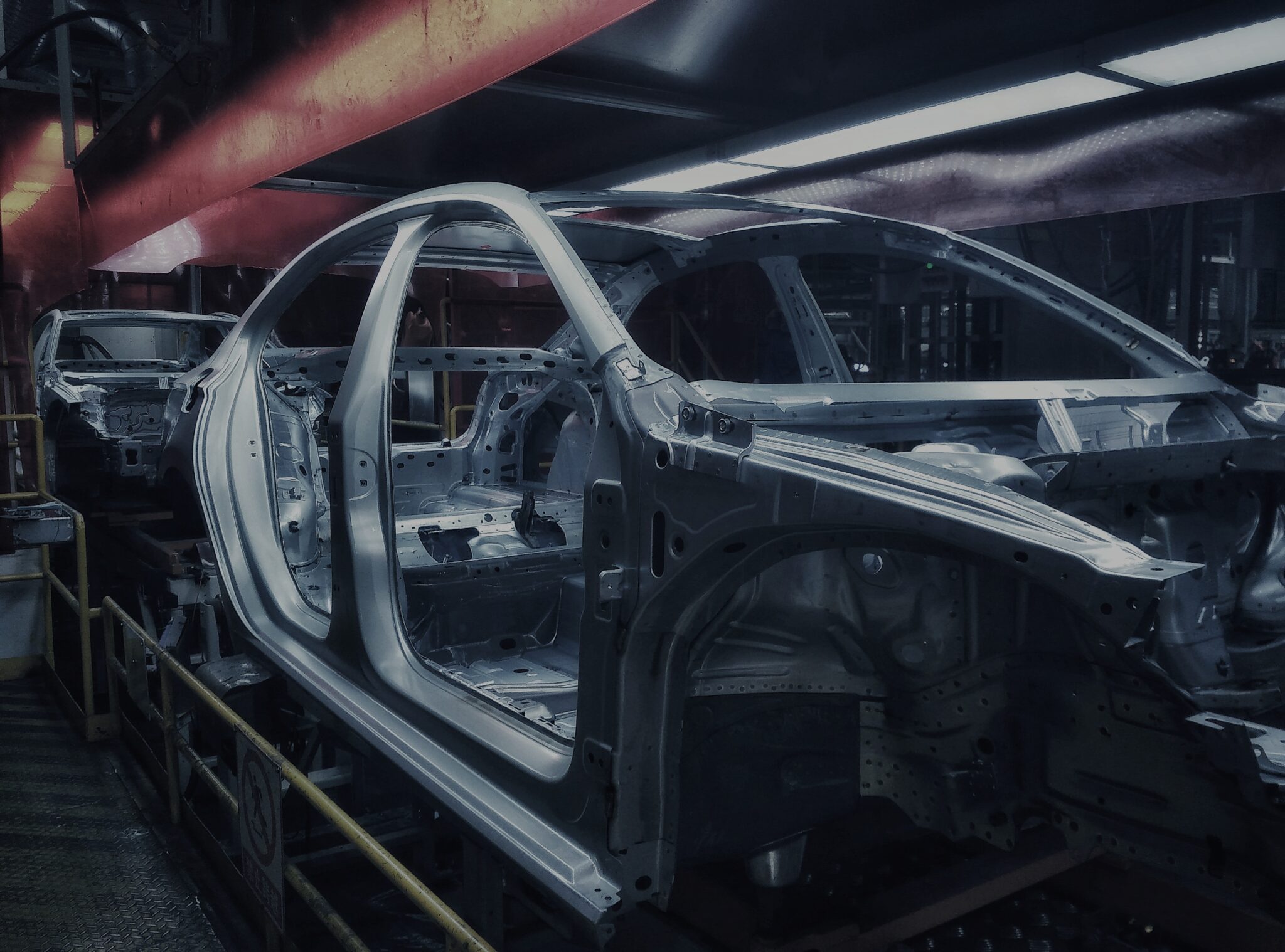
As concerns over driver safety and fuel economy have become more prominent, automotive manufacturers have sought to make all aspects of the vehicle production lifecycle more efficient. Part of this ongoing optimization process includes thoroughly considering the material properties that are most effective or beneficial in automotive applications, and attempting to incorporate more materials that provide these desired characteristics. One key breakthrough in this area has been the development of advanced high-strength steels (AHSS).
Advanced high-strength steels are new generations of steel grades that offer a unique combination of durability, ease of manufacturability, and high strength to weight ratio that ensures steel parts and components meet critical safety and efficiency regulations in a cost-effective manner.
Automakers have been using advanced high-strength steels for years, and as manufacturing processes have improved, so too has each subsequent generation of steels. Using precise heating and cooling processes and different strengthening mechanisms, engineers can achieve optimum mechanical properties — such as high ductility or tensile strength — while also meeting requirements for crash performance, ductility, fatigue, stiffness, and other characteristics.
The various types of advanced high-strength sheet steels provide different properties, as well, which allows manufacturers to tailor their part composition to meet the specific needs of each application. Automobile frames, for instance, require greater stiffness (to maintain the structural integrity of the vehicle) than the parts used in the crumple zone, which are designed to undergo controlled deformations that help protect passengers if a collision occurs.
Steels that have yield strength levels of 550 megapascal pressure units (MPa) or higher are typically considered to be advanced high-strength steels. For the first and second generation of these metals, engineers were quick to leverage the differences in chemical composition and multiphase microstructures of specific steels to meet the performance demands of automotive components.
New research and developments in the past few years have led to the new, third generation of advanced high-strength steels, which are designed to provide increased combinations of strength and ductility, often at significantly lower costs. While the industry is still working toward a standardized definition of third generation high-strength steels, the typical desired properties are a minimum strength of 1200 MPa and a ductility of 30% elongation — a notable increase over earlier generations of steels.
While they’ve been used for years for automotive applications, advanced high-strength steels have also been increasingly incorporated into other manufacturing sectors. The crash safety features of high-strength steels make them ideal for applications in rail transport systems, for instance.
Advanced high-strength steels have also been found to improve engine performance and speed limitations not only for automobiles, but also for aircraft, ships, and trains. The advanced high-strength steel market is also poised to offer significant energy savings to manufacturers worldwide as methods become more efficient.
Advanced high-strength steels do come with some limitations. The increased ductility of third generation advanced high-strength steels requires increasing the alloying content of the metal. This allows the steels to be cold formed into more complex shapes while still retaining material ductility, but leads to increased wear on forming dies and increased springback.
Weldability also presents a challenge, as the microstructures created by higher carbon and alloying content of advanced high-strength steels can be negatively impacted by the rapid heating and cooling involved in the welding process.
One goal in the ongoing development of third generation advanced high-strength steels is to reduce the alloying content of high-strength steels in order to keep costs lower, while also maximizing strength and ductility and avoiding embrittlement.
Advanced high-strength steels may be well-suited to improve the tensile strength and durability of a variety of parts across industries. Advances in energy efficiency and engineering are likely to make the next generation of advanced high-strength steels even more versatile.
SyBridge is the manufacturing partner of choice if you’re looking to manufacture parts using advanced high-strength steels. Our dedicated team of designers and engineers provides on-demand manufacturing services with comprehensive support throughout the product development and manufacturing lifecycles. We work closely with each of our customers to ensure that every part is optimized for design and manufacturability, using the right processes and techniques to create consistently superior products. Contact us today to get started.
Forget typical cycle times. We're pushing the boundaries of conformal cooling. While traditional approaches deliver…
Forget typical cycle times. We're pushing the boundaries of conformal cooling. While traditional approaches deliver…
From left to right: Brayden Janak (apprentice); Logan Vifaquain (CNC machining, Programming and CMM); Ron…
SyBridge Technologies is proud to announce we have been awarded the 2023 General Motors Supplier…
Today, designers and engineers are accustomed to working with digital tools in their day-to-day jobs.…
Optimizing Your Injection Molding Process for Cost-Effective Manufacturing Excellence In today’s competitive landscape, manufacturers are…